Europe Warns Methane Polluters as Bloc Pushes to Slash Emissions
(Bloomberg) -- The European Union aims to slash methane emissions by clinching a deal that could have global ramifications if major energy importers are targeted over leaks of one of the most potent greenhouse gases.
Negotiators from parliament and member states will enter what is likely to be the final round of talks Tuesday over the shape of rules cracking down on methane leaked into the atmosphere by the energy sector. The goal is to get a deal in place before the COP28 climate summit in Dubai later this month.
The rules will require energy companies to regularly inspect infrastructure such as pipelines and oil wells to look for methane — a gas that’s 80 times more powerful than CO2 over a 20-year time frame — escaping into the atmosphere. Differences remain over how big a leak needs to be to require repair, while some EU states are concerned about the implications for energy security.
Applying the rules to imports over the next decade would be one step beyond regulations in countries like Canada and Nigeria. That could have an outsized impact on the climate, because the 27-nation bloc relies on foreign supplies for over 90% of its oil and gas.
“We’re watching you,” Jutta Paulus, the Green lawmaker who is parliament’s lead negotiator, said in a message to fossil fuel companies outside of the bloc. “We want to do something that’s really meaningful for the climate.”
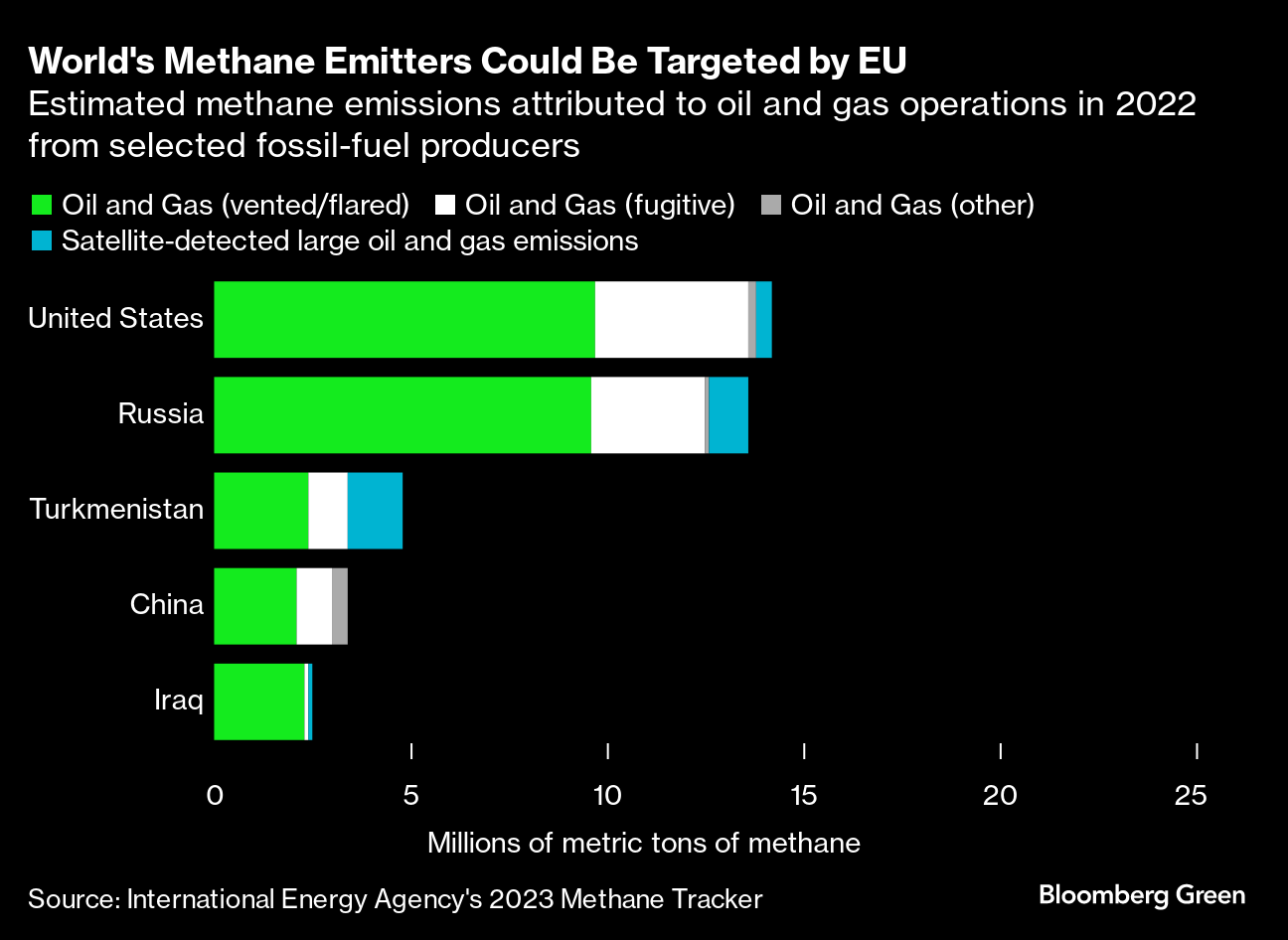
If the EU were to apply the same level of ambition to imports as they do to domestically produced fossil fuel supplies, then global methane emissions in the oil and gas sector could be reduced by at least 30%, according to Clean Air Task Force, a climate non-profit.
However, EU member states are concerned over the possible knock-on impact on the bloc’s security of energy supplies at a time when it is shedding its dependency on Russian fossil fuel imports.
The European Commission, the bloc’s executive branch, has floated gradually phasing in rules so that imports reach a “certain level of methane intensity performance” by the end of the decade, according to a document seen by Bloomberg News. The EU relies on Norway for around 44% of its pipeline gas and on the US for almost half of its liquefied natural gas.
Methane emissions from pipeline gas tend to be higher than for LNG, mainly due to activities in producing countries, according to Berkley Research Group. Algeria makes up around 17% of the EU’s pipeline gas imports. Several super emitting events from the country have been tracked by satellites.
“As the world’s largest natural gas importer, the EU can no longer outsource pollution while claiming climate leadership,” said Flavia Sollazzo, senior director of EU Energy Transition at Environmental Defense Fund Europe. “The bloc’s external ‘methane footprint’ is up to 8 times higher than its domestic emissions.”
Scientists using satellite observations have consistently found that operators and governments significantly under report the climate impact of fossil fuels. A study published in in August found that observed methane releases from global oil and gas operations are 30% higher than estimates provided by countries to the United Nations.
Industry meanwhile is lobbying against stricter rules. Leak detection and repair thresholds being negotiated are equivalent to a fraction of a dairy cow’s methane emissions, while other measures like quantifying emissions from subsea wells are unfeasible, according to the International Association of Oil & Gas Producers.
“The EU Methane Regulation is at risk of being impossible to implement by the European oil and gas industry because of certain requirements that are disconnected from reality,” said Nareg Terzian, head of strategy and communications at the group. “Some requirements rely on technologies that do not exist. Others are entirely disproportionate.”
©2023 Bloomberg L.P.
KEEPING THE ENERGY INDUSTRY CONNECTED
Subscribe to our newsletter and get the best of Energy Connects directly to your inbox each week.
By subscribing, you agree to the processing of your personal data by dmg events as described in the Privacy Policy.
More oil news

Asian Stocks Fall as China’s Confab Disappoints: Markets Wrap

China’s Weak Winter LNG Demand Provides Relief for Rival Buyers

Oil Edges Higher Ahead of US Inflation Figures and OPEC Report

Oil Slips as Glut Outlook Outweighs Optimism on China Stimulus

Oil Edges Higher as Traders Weigh Fallout From Syrian Upheaval

China’s Solar Industry Looks to OPEC for Guide to Survival

Five Key Charts to Watch in Global Commodity Markets This Week

Oil Steadies as OPEC+ Opts Again to Delay Plan to Restore Output

NMDC LTS to acquire 70% equity stake in Emdad
















