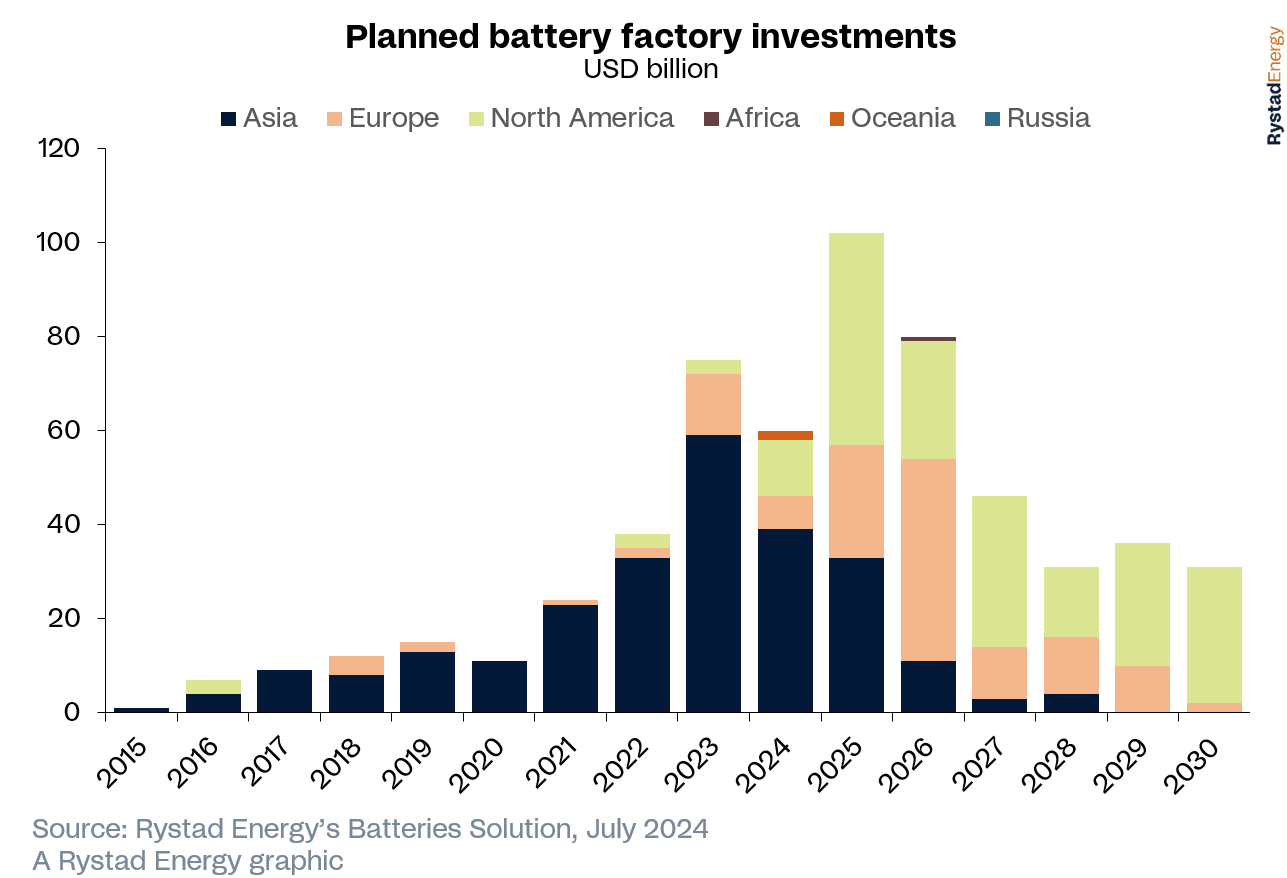
Rise and fall: global battery investments dip for first time since 2020
Following four consecutive years of significant growth, this year is set to see a sizeable decline in global battery investments for the first time since 2020, according to Rystad Energy research. A slump in battery infrastructure investments in mainland China is largely responsible for the global slowdown, as the Asian economic powerhouse navigates phases of growth driven by policy change, increased electric vehicle (EV) adoption, supply shortages, rising raw material costs and rapid capacity expansion.
A global leader in battery dynamics, China has maintained its position in lithium-ion battery (LIB) development, largely attributed to its early adoption of industrial-scale projects and rapid production growth to match its ambitious EV expansion plans. As a result, production surged more than 40% in both 2021 and 2022. Despite the pace of annual growth slowing from 2022 onwards, this is a consequence of maturity and sustained capacity expansion. With the nation achieving self-sufficiency in battery supply, China’s attention has turned strategically towards Europe and the US, where major manufacturers are progressing from planning to production, albeit still at a nascent stage of development.
In Europe, the interdependency of EVs on LIB production underscores the concern raised by investment declines this year. This downturn is primarily driven by diminishing EV market demand, which in turn poses risks of project delays and cancellations in EV infrastructure. These challenges highlight broader issues in the EV sector, evident in the financial reports and stock prices of original equipment manufacturers (OEM) globally, including Chinese manufacturers that are facing profitability issues. Furthermore, subsidies incentivize sector growth, yet high energy costs, labor expenses and bureaucratic hurdles impede progress for the industry at large.
In contrast, the US has seen exponential growth in lithium demand amid increasing concerns over secure supply chains. Despite efforts to ramp up LIB production, both Europe and the US struggle with nascent industrial infrastructure. To mitigate reliance on Chinese supply chains for critical minerals, both Europe and the US are implementing policies to bolster energy security. Looking ahead, China's stronghold in global battery investment and lithium trade appears secure due to its primary access to essential resources.
"China's dominance in battery investment and lithium trade seems unshakeable for the foreseeable future, given their control over key resources. However, building a battery factory from scratch takes years and navigating local regulations adds even more time. This means the market two years from now remains unpredictable. Collaboration across the entire supply chain is crucial for the industry's health." says Duo Fu, Vice President, Battery Market Research, at Rystad Energy.
China’s domestic industry is undergoing consolidation as it aims to offer higher-quality battery products in the form of diversified technological advancements. Despite a surge in investment in recent years that fueled rapid LIB capacity expansion, a slowdown in demand has prompted some companies, particularly those from non-traditional sectors unable to compete on price, to exit the market. Moving forward, mere capacity expansion will prove inadequate without robust technical support.
The LIB sector is witnessing a surge in innovative technologies focused on cost savings, enhanced energy density and improved safety measures. Amid these developments, the LIB sector faces challenges of insufficient high-quality production capacity, although robust companies continue to expand. As the sector enters a period of adjustment, technological innovation emerges as the linchpin for its future development.
Reflecting these shifts, Chinese LIB company stocks peaked in early 2022 before gradually declining. This year, 32 listed companies in China's lithium battery sector forecast 2024 earnings ranging from a net loss of CNY 580 million ($80 million) to a profit of CNY 2.822 billion ($397 million), marking a significant year-on-year decrease. Consequently, the enthusiasm for LIB investment has waned, ushering in a phase of stability as the sector matures.
Alternative battery technologies are gaining momentum, with cost-effective solutions such as lithium iron phosphate (LFP) batteries emerging as attractive options. Tesla has announced a partnership with CATL to ramp up mass production of LFP batteries through a license royalty service (LRS), while Ford is reportedly exploring a similar strategy. Mercedes and Stellantis have paused their European EV battery factory projects to reconsider their approach, potentially shifting towards more affordable LFP cells. Additionally, three South Korean battery factories have outlined plans to increase LFP cell production capacity.
Advancements in battery technology include the development of new materials such as composite copper foil, silicon-based anode materials, high-nickel cathode materials like lithium ferromanganese phosphate (LFMP) and lithium bis(fluorosulfonyl)amide (LIFSI). These innovations aim to lower costs and enhance efficiency. Improvements in battery structural systems, such as the introduction of larger-sized 4680-cylinder batteries and solid-state batteries, are also under way, potentially altering the capabilities and longevity of batteries in future markets.
KEEPING THE ENERGY INDUSTRY CONNECTED
Subscribe to our newsletter and get the best of Energy Connects directly to your inbox each week.
By subscribing, you agree to the processing of your personal data by dmg events as described in the Privacy Policy.















