Toyota Sees Way for Future EVs to Drive Like the $375,000 Lexus LFA
(Bloomberg) -- On the face of it, an electric vehicle with a manual transmission makes no sense.
EVs don’t have the driveshafts or gears that internal combustion engines need to accelerate from a stop. Instant torque is available at any speed. Many will tell you this is all part of the appeal of battery-electric vehicles — they’re less complicated.
But in an ironic twist, the automaker synonymous with the merits of eliminating waste and unnecessary work is OK with the idea of the stick shift staying around.
Toyota has built a prototype Lexus UX 300e with a gear shifter and clutch pedal that mimics the manual-transmission experience. Those two components aren’t connected to anything mechanical — they’re effectively no different from joysticks for video games.
Although Toyota engineers first briefed journalists on this concept months ago, it wasn’t until last week that the carmaker gave analysts and reporters a chance to experience the sensation of switching gears in an EV for themselves at its research facility on the foothills of Mount Fuji, a few hours from Tokyo.
Having been assailed by critics for squandering its lead in electrification to the likes of Tesla and China’s BYD, the test drives were part of an all-out effort by Toyota to open up about how much work it’s been putting into EVs behind the scenes. The carmaker gave detailed briefings last week on battery development, production plans and related technology. Other concepts available to take for spins included a hydrogen-burning Lexus SUV, a steer-by-wire Lexus RZ, a hydrogen fuel cell delivery truck and a battery-powered kei delivery van.
In the category of what Toyota is calling the Electrified Sport Concept, the carmaker also showed off a Lexus RZ 450e that can change the behavior of its powertrain on the fly to mimic anything from a Passo compact, to a delivery van, to a $375,000 Lexus LFA supercar.
All of this can be simulated via software, although Toyota’s engineers sought to enhance the experience with a speaker mounted — somewhat clunkily — on the floor under the driver’s seat. There was a bit of a lag between depressing the pedal and the artificial din of an LFA’s 4.8-liter V10 revving up, but the concept was clear.
Adding tenors to electric cars isn’t a new idea. Traction motors are usually tuned to emit a specific sound at a noticeable volume, both to alert pedestrians and add a little character to the driving experience. Brands ranging from Ferrari to Dodge have been working on fake exhaust noises for EVs they have in the pipeline.
Standing across from Toyota’s EVs — the one with a manual transmission and the other with split personalities — I asked Chief Technology Officer Hiroki Nakajima how serious he was about bringing these concepts to market. The cost of doing so wouldn’t be significant, he told me.
“The truth is, manual EVs and on-demand battery EVs can actually be put out as products,” Nakajima said later on, during a Q&A session. “Because it’s just changing the software.”
So what was it like to drive an EV with a manual transmission? It was uncanny, to say the least. The “engine” — which, again, didn’t exist — stalled in a convincing manner, though it was ready to go again in less than a second. The Toyota engineer sitting next to me encouraged me to “rev” the car and take off from a stop at full pedal.
I found myself imagining new possibilities — for example, a vehicle that rides like a limousine when stuck in heavy traffic, but transforms into a six-speed Supra on the highway. Combine the concepts and you might even be able to create a car that doesn’t exist, such as a stick-shift Lexus LFA.
Whether these ideas make their way to products in the real world will depend on demand, and how much car buyers are willing to pay for the pleasure. There’s probably more that Toyota can do to alter the steering, braking and suspension characteristics to simulate different cars, Nakajima said.
Do these ideas amount to solutions in search of a problem? Or, as one colleague quipped, will these cars with faux-manual transmissions be the vegan burger of the auto world — faux red meat for the petrol heads?
We’re unlikely to find out until at least 2026, when Toyota plans to start rolling out its next generation of EVs.
©2023 Bloomberg L.P.
KEEPING THE ENERGY INDUSTRY CONNECTED
Subscribe to our newsletter and get the best of Energy Connects directly to your inbox each week.
By subscribing, you agree to the processing of your personal data by dmg events as described in the Privacy Policy.
More renewables news

GE Vernova to Power City-Sized Data Centers With Gas as AI Demand Soars

Longi Delays Solar Module Plant in China as Sector Struggles

Australia Picks BP, Neoen Projects in Biggest Renewables Tender

SSE Plans £22 Billion Investment to Bolster Scotland’s Grid
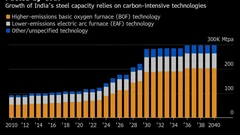
A Booming and Coal-Heavy Steel Sector Risks India’s Green Goals

bp and JERA join forces to create global offshore wind joint venture

Blackstone’s Data-Center Ambitions School a City on AI Power Strains

Chevron Is Cutting Low-Carbon Spending by 25% Amid Belt Tightening

Free Green Power in Sweden Is Crippling Its Wind Industry
















