Petrobras Captures Carbon to Ramp Up Gas Production, and Calls It Green
(Bloomberg) -- Brazil’s state-controlled oil giant Petrobras is capturing and storing a growing amount of carbon dioxide below the seabed in a strategy that helps it boost oil and natural gas production. It also calls it green.
The company is pursuing the strategy at three giant offshore oil fields located 230 kilometers (143 miles) off the coast of Rio de Janeiro. There, Petrobras uses specialized membranes to separate CO2 from natural gas that is produced as a byproduct of oil extraction. It then injects the carbon back into the reservoir.
The technique increases underground pressure in the reservoirs, which makes it easier to bring more oil to the surface and extends the life of the fields. Removing the CO2 also allows Petrobras to safely pipe the remaining natural gas to shore. Otherwise, it could cause potential leaks because C02 produces carbonic acid that corrodes steel pipelines, and Brazil’s offshore gas has high levels of the contaminant.
“It’s driven by operational concerns. It has nothing to do with environmental consciousness,” said Cleveland Jones, a consultant and researcher at the National Institute of Oil and Gas in Rio de Janeiro. “They shouldn’t take any credit for it.”
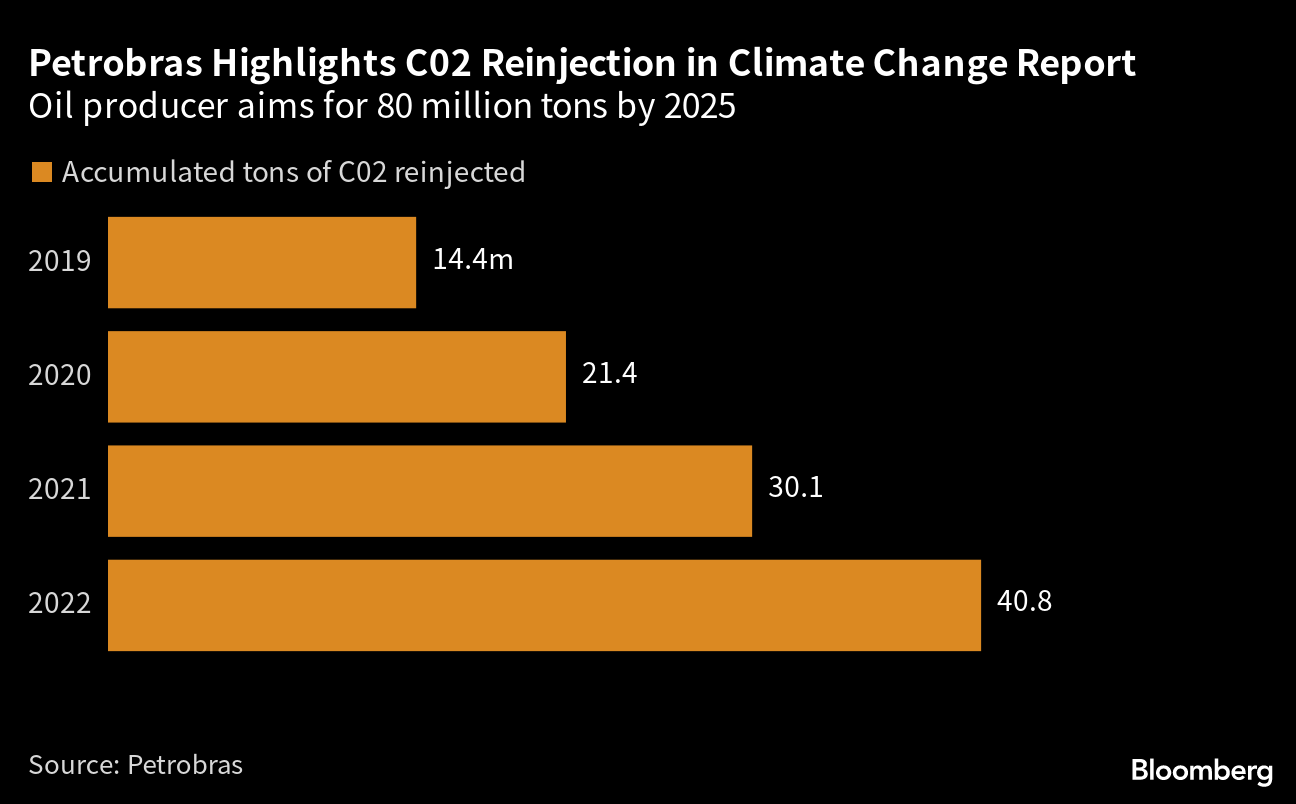
Yet in its most recent sustainability report, Petrobras highlights how the carbon capture program reduces emissions intensity, or the amount of greenhouse gases emitted per barrel of production. It also lists carbon capture as one of its major green technology achievements. In the late 2000s, Petrobras developed the technology as the most feasible way to get the gas from the middle of the ocean to end users on land.
Carbon injection can have a net positive impact on the climate if the carbon is captured from the atmosphere or industrial sources as opposed to reinjecting CO2 that was in the ground to begin with. The latter, though, is what’s used widely throughout the oil industry to increase fossil fuel extraction.
Brazilian policies governing fossil fuel operations also forced Petrobras’s hand: Flaring or venting the CO2 separated from the natural gas would break Brazilian regulations. To bring the natural gas ashore and avoid corroding its pipelines, Petrobras had to find a technical solution.
In response to questions, Petrobras clarified that it isn’t including the carbon reinjection program — known as carbon capture, utilization and storage — as part of its net emissions reduction or as a potential source of carbon offset credits. Still, the company highlights how it plans to reinject an accumulated 80 million tons of CO2 from 2015 through 2025 as a major advance in its climate commitments.
“We have the largest offshore CO2 reinjection program in the world,” it said in its climate change report.
Petrobras has two pipelines where carbon capture is deployed to clean the natural gas coming from deepwater fields and expects to bring a third pipeline into production next year. That could lift supplies by as much as 21 million cubic meters a day and ease Brazil’s reliance on expensive imports of liquefied natural gas from Bolivia, which has become an unreliable supplier of the power-plant fuel.
Petrobras produces oil that is comparatively low in carbon, both from the amount of energy used to produce the oil, and the chemical makeup of the oil itself. A single well in Brazil’s so-called pre-salt offshore region can produce more than 50,000 barrels a day, while it takes more than 5,000 wells to produce the same amount in Texas’s famed Permian Basin. This means it takes less energy and emissions in Brazil to produce the same amount of oil. That's in part due to the company's use of C02 to boost the efficiency of its wells.
While many producers are making efforts to cut pollution on-site, the majority of a barrel of oil’s greenhouse gas emissions are produced when it's burned by consumers for transportation or energy.
Petrobras also says that more than a decade of experience in CO2 reinjection will help it move into new types of carbon storage, such as capturing emissions from refineries and then storing them in decommissioned oil fields, which would be a potential source of carbon credits. The oil industry has been advancing carbon capture and storage projects as a way to counter its emissions. Occidental Petroleum Corp. is capturing carbon from the atmosphere and injecting it into oil fields as part of a plan it says will eventually make its crude net zero in emissions.
Other oil majors have encountered difficulties getting carbon capture to work. Chevron’s carbon capture and storage project in Australia, Gorgon CCS, is only injecting a third of the carbon that it is supposed to and faces years of work ahead to reach full capacity. The project was designed to capture 4 million tons of C02 a year from a liquefied natural gas plant and store it in a subsea reservoir.
Carbon capture will need to grow to reach net zero by 2050 if the world is to avoid warming more than 1.5C, according to numerous lines of research. While more than $7 billion was invested in carbon capture projects between 2018 and 2021, more than 70% of all captured CO2 is being used for enhanced oil recovery, BloombergNEF said last year in a research report. The report also said that fossil fuel companies’ use of carbon capture for oil extraction over more than 30 years has contributed to a lack of social acceptance of the technology.
©2023 Bloomberg L.P.
KEEPING THE ENERGY INDUSTRY CONNECTED
Subscribe to our newsletter and get the best of Energy Connects directly to your inbox each week.
By subscribing, you agree to the processing of your personal data by dmg events as described in the Privacy Policy.
More renewables news

Longi Delays Solar Module Plant in China as Sector Struggles

SSE Plans £22 Billion Investment to Bolster Scotland’s Grid
A Booming and Coal-Heavy Steel Sector Risks India’s Green Goals

bp and JERA join forces to create global offshore wind joint venture

Blackstone’s Data-Center Ambitions School a City on AI Power Strains

Chevron Is Cutting Low-Carbon Spending by 25% Amid Belt Tightening

Free Green Power in Sweden Is Crippling Its Wind Industry

California Popularized Solar, But It's Behind Other States on Panels for Renters

A $50 Billion London Investor Takes a Contrarian View on Trump
















