Explained: the renewed interest in complex gas projects as $44b Alaska LNG nears FID
The massive Alaska LNG project that aims to deliver natural gas from Alaska’s North Slope fields via a 1,300km pipeline, moved closer to a final investment decision (FID) this week with the selection of Worley as the contractor for additional engineering and preparing a final cost estimate.
What’s the latest development on Alaska LNG?
Glenfarne Alaska LNG, a subsidiary of Glenfarne Group, LLC, and majority owner and lead developer of Alaska LNG, said on Wednesday it has selected Worley to undertake additional engineering and prepare a final cost estimate for the Alaska LNG pipeline in sufficient detail to achieve FID.
The work for this has commenced and will utilise and supplement the extensive package of previously completed engineering work and update the cost of the pipeline, Glenfarne said in a statement. Worley has also been selected as the preferred engineering firm for the Cook Inlet Gateway LNG import terminal and project delivery advisor to Glenfarne across the Alaska LNG projects, it said.
Why is the Alaska LNG project so critical for gas infrastructure?
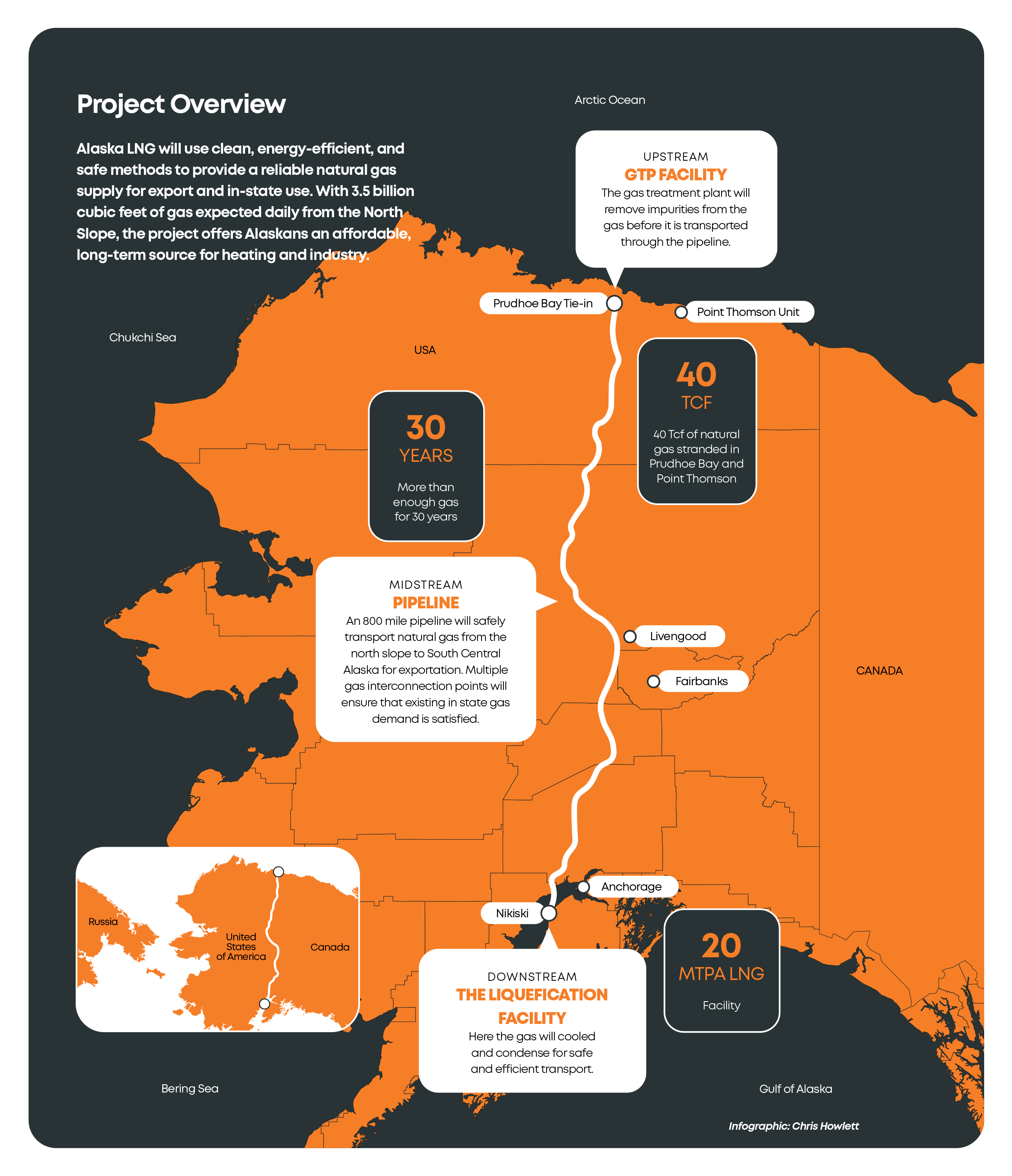
Alaska LNG – an integrated natural gas project – is one of the most important ones being built in the United States and aims to provide energy for both domestic use and export to Asian markets. The $44 billion project will use clean, energy-efficient, and safe production methods to deliver a stable supply of natural gas for commercialisation and for in-state distribution.
The project, being developed by the Alaska Gasline Development Corporation, is expected to deliver from the North Slope gas fields on average about 3.5 billion cubic feet of gas per day, much of it for international markets.
Who are the project partners for Alaska LNG?
Concurrently with the final engineering work, Glenfarne has launched a strategic partner selection process to partner with global companies that support Glenfarne’s execution efforts and have complementary expertise to help deliver the Alaska LNG project, the company said.
“Glenfarne is pushing Alaska LNG forward with expediency engaging prospective strategic partners. We are particularly proud to be expanding our relationship with Worley to Alaska LNG from our existing partnership on the Texas LNG project. Worley is one of the world’s largest and most experienced engineering and project delivery firms with a long history of success in Alaska,” Brendan Duval, CEO and Founder of Glenfarne Group, said in a statement.
How viable is the project and what are the expected timelines?
A Wood Mackenzie study in 2023 found that the complex Alaska LNG is economically viable and can deliver LNG to Asia at prices lower than competing US Gulf Coast projects.
Construction for the LNG pipeline would begin in 2026 with gas flowing in 2028, and the conditioning plant and export facility completed in 2030, according to Alaska Governor Mike Dunleavy. By bypassing the Panama Canal, it would potentially transform energy trade routes between North America and Asia. The project involves constructing a pipeline from fields north of the Arctic Circle to southern Alaska, where the gas would be cooled into liquid form and shipped on tankers.
Why are Japan and Korea considering investment in the project?
Japan and South Korea are among the countries considering investing in the $44 billion LNG project, and the US is seeking a summit to discuss the project with Japan and South Korea’s energy ministers on June 2. South Korea said on Thursday it will send its Deputy Minister for Energy Policy and other energy ministry officials to the Alaska Sustainable Energy Conference in early June.
For Asian countries, shipping LNG from Alaska would offer cost and time advantages compared to traditional sources in Australia, the Middle East and the US Gulf Coast. However, potential buyers have historically expressed caution about the project’s substantial costs and viability.
Japan’s top power generator JERA, the world’s second-largest LNG buyer after China, is considering the $44 billion project as a potential source of LNG supply. JERA sources about 10% of its LNG from the US and purchases around 35 MMT of LNG annually.
How strong is the federal support for Alaska LNG?
The Alaska LNG project has benefitted from robust federal support. Legislation originally signed by President Joe Biden makes the project eligible for approximately $30 billion in federal loan guarantees, greatly reducing borrowing costs, making Alaska LNG competitive in global markets.
The project also enjoys robust support from President Trump, who has made Alaska LNG a centerpiece of his second term through his executive orders and a focus of the new National Energy Dominance Council to use the full force of the federal government, including defence, trade, and commerce tools, to support Alaska LNG.
The US Department of Energy has highlighted multiple benefits of the Alaska LNG project, including job creation, enhanced energy security for the United States and allies, and an estimated $10 billion annual reduction in the US trade deficit. According to US Energy Secretary Chris Wright, all options for supporting the project are on the table, including a potential loan guarantee from the DOE’s Loan Programs Office.





