Tesla's Shrewdest Product Is Proving to Be Its Charging Network
(Bloomberg) -- Chris Bowe needed a quick charge before climbing over the Santa Cruz Mountains in his Ford F-150 Lightning on his drive home to the San Francisco Bay Area.
So he pulled into Tesla's Supercharger station in Scotts Valley, which has 16 stalls. It’s one of just two locations on the West Coast that is open to drivers with the latest innovation from Tesla Inc.: the Magic Dock.
The Magic Dock is a Tesla connector that allows other EVs to use the company’s extensive charger network. It is hardware that is added to the charging station itself: There’s no need for drivers to carry an adapter in the trunk.
“I plug it into my truck, and it just works,” said Bowe, 49, a senior manager at FedEx. “You hear the Magic Dock click and latch into place and it starts charging. It’s beautiful.”
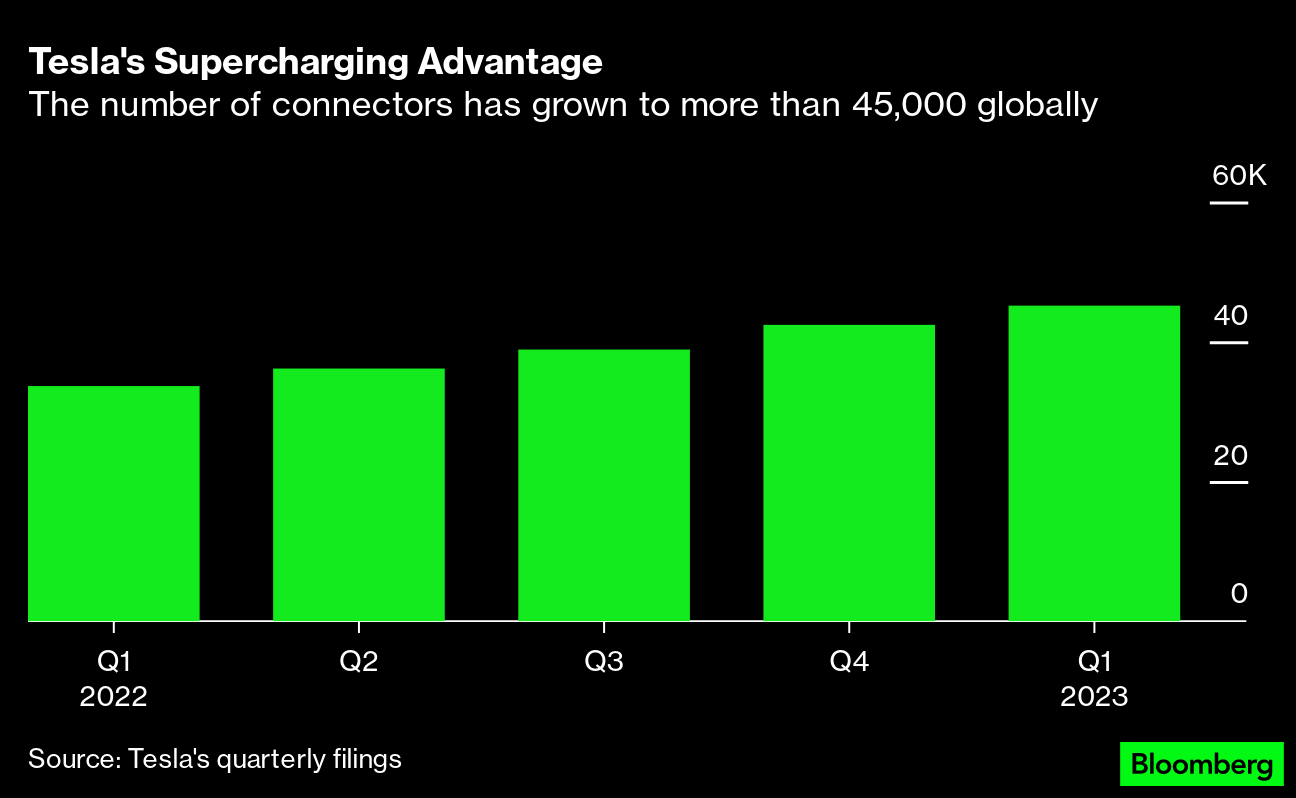
Tesla, which is headquartered in Austin, is known for its sleek electric cars. The company led by CEO Elon Musk sold more than 1.3 million vehicles globally in 2022 and aims to sell at least 1.8 million in 2023. The first Blade Runner-esque Cybertrucks are slated to be handed over later this year.But Tesla’s low-key and ubiquitous Superchargers, which now cover much of North America, Asia, Europe and the Middle East, are proving to be the shrewdest, and most strategic, product of all. Tesla dominates EV sales in the US and, not surprisingly, is conquering reliable fast charging. At the end of the first quarter, the company had nearly 5,000 charger stations—and more than 45,000 charging stalls or connectors — globally, according to company filings. Many are located off of freeways in shopping plazas, and often have several stalls for charging. Tesla did not respond to inquiries for this story.
But it’s not just the Magic Dock. In recent weeks, two of Tesla’s biggest rivals—Ford Motor Co. and General Motors Co.— announced that they are partnering with Tesla on charging. In both cases, Ford and GM customers can buy a Tesla-made adapter that will allow them to access more than 12,000 Superchargers starting in early 2024. And in 2025, Tesla’s unique charging port will be built into Ford’s and GM’s electric vehicles. Selling a car is one thing; selling consumers an EV fueling experience is another, and one that provides an ongoing revenue stream. Tesla could potentially earn as much as $3 billion by 2030 from the Ford and GM charging deals, according to Piper Sandler & Co.
Mary Barra, the chief executive officer of GM, joined Musk on Twitter— which Musk owns— on Thursday to announce her company’s new partnership. “Not only will it help make the transition to electric vehicles more seamless for our customers, but it could help move the industry toward a single North American Charging Standard,” she said.
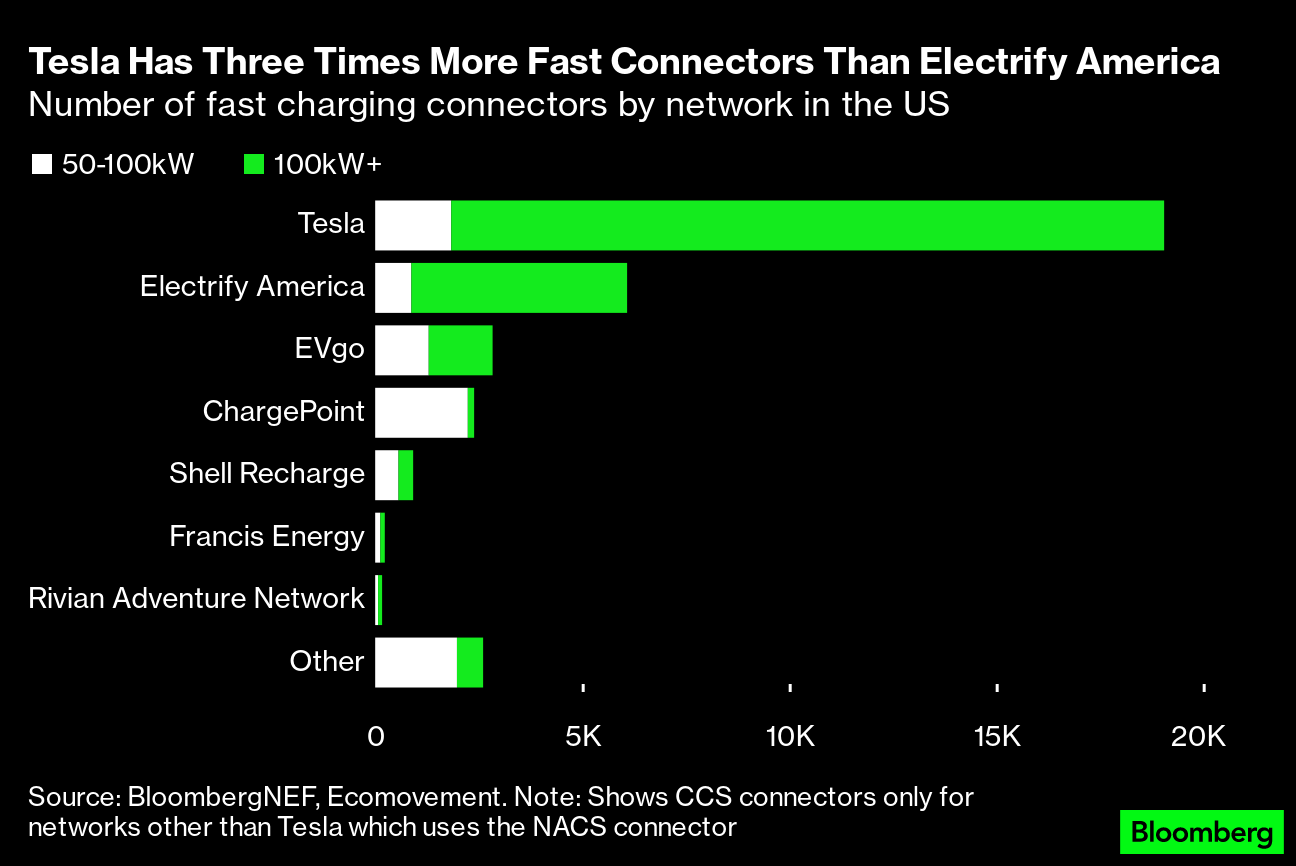
In unveiling his company’s deal in May, Ford Chief Executive Officer Jim Farley mentioned “reliability” more than once and said he was “really pumped.”“We don’t want the Tesla Supercharger network to be like a walled garden,” said Musk during the event with Farley. “We want to be supportive of electrification and sustainable transport in general.”Tesla is the largest installer of ultra-fast chargers in the US, according to BloombergNEF, accounting for 71% of installations in 2022. BNEF’s latest Electric Vehicle Outlook 2023, published June 8, forecasts that electric models in the US will make up nearly 28% of passenger vehicle sales by 2026, up from 7.6% in 2022. But more EVs on the roads means that more cars will be sharing the nation’s chargers. In its report, BNEF said that support for charging infrastructure needs to be expanded “dramatically, including for remote and otherwise under-served locations.”
The White House—eager to spur adoption of EVs—announced the federal National Electric Vehicle Infrastructure program earlier this year, which allocates $5 billion to states to build out fast charging. As part of that announcement, Tesla pledged to make at least 3,500 new and existing Superchargers open to non-Tesla EVs.“We have understood since day one that a great charging experience is the linchpin to electric vehicle adoption,” said Rebecca Tinucci, who leads Tesla’s charging infrastructure team, at the company’s Investor Day in March. “Getting here meant we spent 10 years building charging infrastructure when basically no one else in the industry would do it.”

In September 2012, Musk unveiled Tesla's first six Superchargers. Constructed in secret, the early sites were along California highway corridors in cities like Folsom and Gilroy. Forget range anxiety: Tesla wanted to make it easy for its customers to go on long road trips.
“This is not some figment of the imagination,” Musk said during the splashy launch event at Tesla’s design studio near Los Angeles. “I think this day will actually go down as being quite historic. I want you to get out there and spread the word. People have this idea that if you have an electric car that you have no freedom, that you’re stuck. There's this idea that you can’t go anywhere. What we’re showing here today is that you have more freedom than anything.”
Why So Many Electric Car Chargers in America Don't Work
“From a marketing standpoint, Tesla’s Superchargers are a huge advantage,” said Owuraka Koney, managing director at Jennison Associates LLC, a major investor that has held Tesla shares since 2011. “Range anxiety is still an issue for consumers, and access to Supercharging helps to drive demand for Tesla right now.”

On my 880-mile round trip drive to and from LA, I charged the car five times: at Harris Ranch, and once in downtown LA. On the way home, I took the far slower but more scenic Highway 101 route, charging in Oxnard, San Luis Obispo and Gilroy. The Model Y preconditioned the battery as I navigated to the nearest charger, and every charger worked.

Tesla, which has $22 billion in cash, is aggressively expanding its network and adds new locations nearly every day. The company is working on quicker charge times, as well as a trip planning feature that optimizes Supercharging site utilization.Tinucci ended her presentation at Investor Day with an architectural rendering of a Tesla-branded drive-in diner with Superchargers and an outdoor movie theater. It’s not just fantasy: Tesla has filed planning documents for a Tesla West Hollywood Diner with the city of Los Angeles.
Tesla has long pushed the envelope of what the fueling of the future will be. But now Tesla customers will have to share the network that has been theirs, exclusively, for so long. It remains to be seen how this culture clash will play out. Will Tesla continue to roll out the Magic Dock? Will Tesla enact a two-tiered billing system: one charging rate for Tesla owners, and a second, more expensive rate for Ford and GM customers? Will the Kettleman City lounge eventually open to non-Tesla owners?
The Magic Dock offers some lessons. The charging port on a Tesla is on the driver’s side of the vehicle, in the back, so you back up close to the Supercharger. But most other EVs on the road today have their charging ports located at the front of the car.
“I was very aware that I am not a Tesla owner,” said Bowe of charging his Ford Lightning in Scotts Valley. “I had to pull nose-in and use the stall to my right, when the correct stall would have been the one to the left. So basically I was taking up two spots, and was using the ‘wrong’ charger.”John Gartner says that Tesla must strike a balance: Keep their loyal Tesla customers happy, while sharing the Supercharging bounty with other electric vehicle owners.“At what point do you dilute the customer experience?” said Gartner. “If you open it up to everyone, then it’s no longer special.”
©2023 Bloomberg L.P.





