Rystad Energy's oil macro market update: oil’s bearish streak continues
Oil market sentiment remains bearish this week, influenced by decelerating oil demand growth and reduced geopolitical risks, pushing prices down. Brent crude oil futures fell into the US $76 per barrel range earlier today, pushed down by ongoing ceasefire talks in Gaza and concerns over weakening Chinese demand.
“The oil market’s recent poor form is continuing this week as a ceasefire in Gaza grows more likely and China demand weakness shows little sign of recovery. Despite ongoing ceasefire negotiations, clashes between Israel and Hamas continue, and the markets will remain highly sensitive to any developments in the region. If the market fundamentals don’t break this bearish trend soon, OPEC+ may be hesitant to unwind their voluntary cuts anytime soon, ” Svetlana Tretyakova, Senior Analyst at Rystad Energy, said.
Additionally, China's economic slowdown, marked by falling growth, home prices and rising unemployment, has led to reduced refinery runs and lower oil demand. In response, both OPEC and the International Energy Agency (IEA) have revised down their 2024 global oil demand forecasts.
Secretary Blinken has urged Israel and Hamas to seize what may be the last chance for a ceasefire and hostage deal, but the situation remains tense with ongoing violence and skepticism about reaching an agreement. Blinken's visit also comes amid pressure on President Biden’s stance on the conflict, which could affect democratic party support in key US states in the upcoming elections.
In China, weak demand and trade tensions are straining the economy, and existing stimulus measures have been insufficient to turn their fortunes around. Inflation is expected to remain low, contributing to lowered global oil demand forecasts by the IEA and OPEC.
Macroeconomic data released in July shows China's consumer prices increased by 0.5% year-on-year, driven by higher food costs, while core inflation rose 0.4%. Producer prices fell 0.8%.
For the US, July's Consumer Price Index (CPI) data met expectations with a 2.9% year-on-year increase and a 0.2% month-on-month rise. Core inflation also decreased to 3.2% year-on-year. Although inflation is cooling, it does not warrant immediate changes in the Federal Reserve policy. Discussions on rate cuts may arise in September, but any adjustments will likely be gradual.
In the energy sector, potential rate cuts could have mixed effects. While they might lower debt costs and ease financial pressures for capital-intensive sectors like hydraulic fracturing, they could also intensify competition for labor and materials.
The July CPI data highlights the need for ongoing vigilance and careful analysis by both policymakers and industry stakeholders.
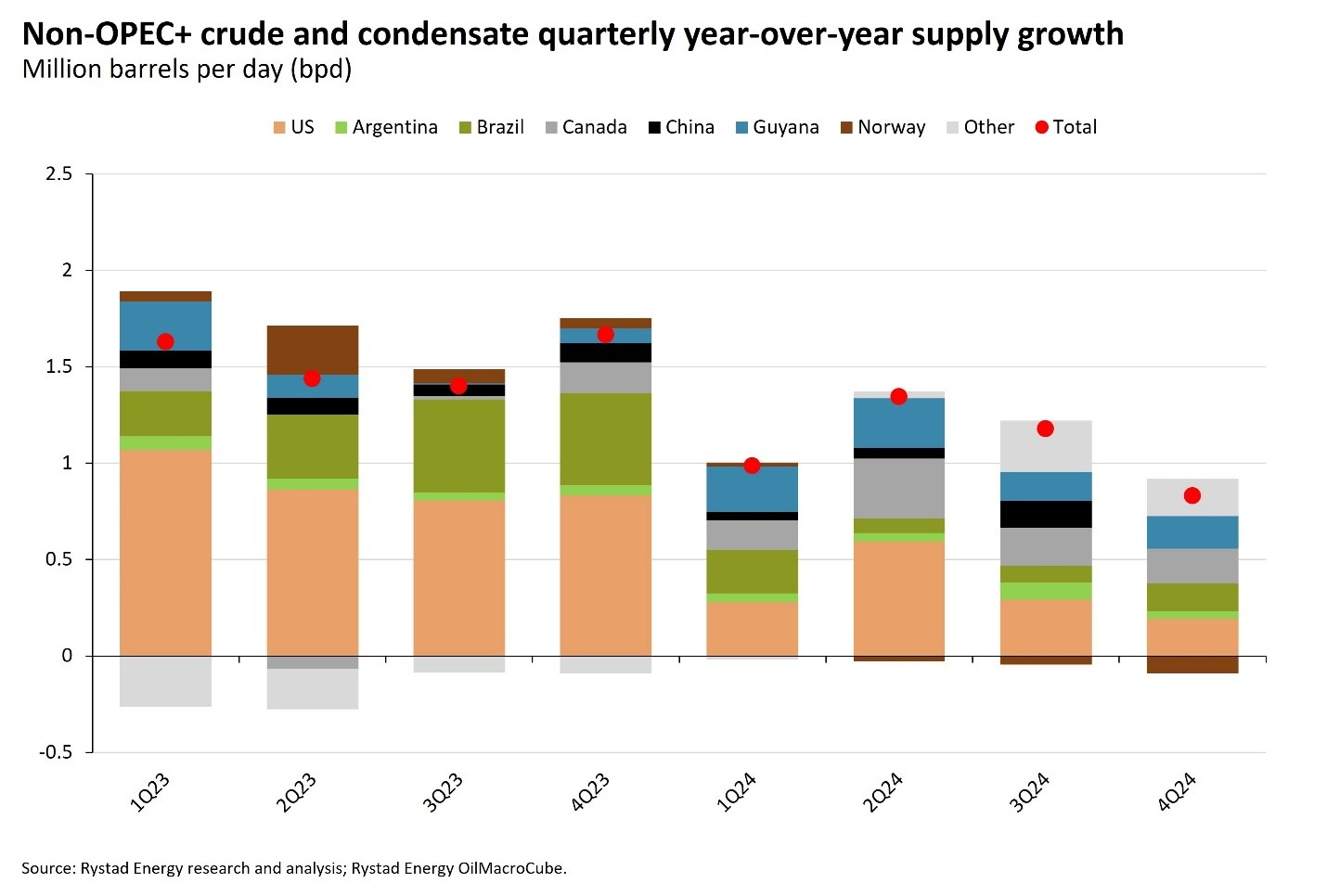
Rystad Energy's updated supply outlook for August indicates North America's crude oil and condensate production is expected to average 20.07 million barrels per day (bpd), down by 136,000 bpd from the previous month. Despite this drop, the US's growth prospects remain strong, with New Mexico's Delaware and Eagle Ford regions leading the increase. However, the Bakken faces a decline due to reduced drilling activity.
The Permian Basin's growth is slowing. Canada is undergoing a major maintenance period from August to October, which could impact global heavy crude supply, particularly to the US and Asia. Canadian exports to China increased in June but may fall in the third quarter.
Mexico's output remains stable at 1.88 million bpd, though exports, especially to India and South Korea, have decreased. The Olmeca refinery's gradual ramp-up might further limit US export availability, affecting North American heavy crude prices.
Latin America is emerging as a key global supply growth driver, producing around 57% of medium-sweet and regular crudes. Brazil, Guyana and Argentina are notable year-on-year growth leaders. Brazil is expected to recover production levels after a slow start to the year. Guyana’s Stabroek block continues to boost regional growth, although July will see maintenance on the Liza field. Argentina’s Vaca Muerta Shale is also growing steadily.
Russia has managed to sustain its oil production and exports despite Western sanctions and OPEC+ cuts, although it has faced challenges with its oil cash flows. Recent data shows that Russia has been increasing crude exports by drawing down stocks and adjusting seaborne and pipeline flows.
However, ongoing compliance issues with OPEC+ production targets and low crude stocks pose risks to sustaining export levels above 3 million bpd. Despite these hurdles, the Urals discount is at its lowest since the EU embargo, indicating market strain. Future Russian oil supply dynamics will hinge on production, export levels, and compliance with OPEC+ targets, along with geopolitical factors such as Ukrainian drone attacks and refinery disruptions.
KEEPING THE ENERGY INDUSTRY CONNECTED
Subscribe to our newsletter and get the best of Energy Connects directly to your inbox each week.
By subscribing, you agree to the processing of your personal data by dmg events as described in the Privacy Policy.















